Spectrophotometric calibration¶
The spectrophotometric calibration adjusts the relative strength of the signal as a function of wavelength. The throughput of the instrument is not the same at all wavelength. We have measured that relative difference earlier when we calculated the sensitivity function. Now we are going to apply that function to correct our science spectra.
As before, we first set some important variables.
sensfunc = '../calibrations/ltt4364_629_20060331_sens'
extinction = 'onedstds$ctioextinct.dat'
observatory = 'Gemini-South'
Then, we call gscalibrate.
imdelete('cstxeqxbrg@sci.lis', verify='no')
for sci in iraf.type('sci.lis', Stdout=1):
sci = sci.strip()
iraf.gscalibrate('stxeqxbrg'+sci, sfunction=sensfunc, \
obs=observatory, extinction=extinction, \
fl_ext='yes', fl_vardq='yes')
We can have a look at the spectra.
for sci in iraf.type('sci.lis', Stdout=1):
iraf.gfdisplay('cstxeqxbrg'+sci, 1, version='1')
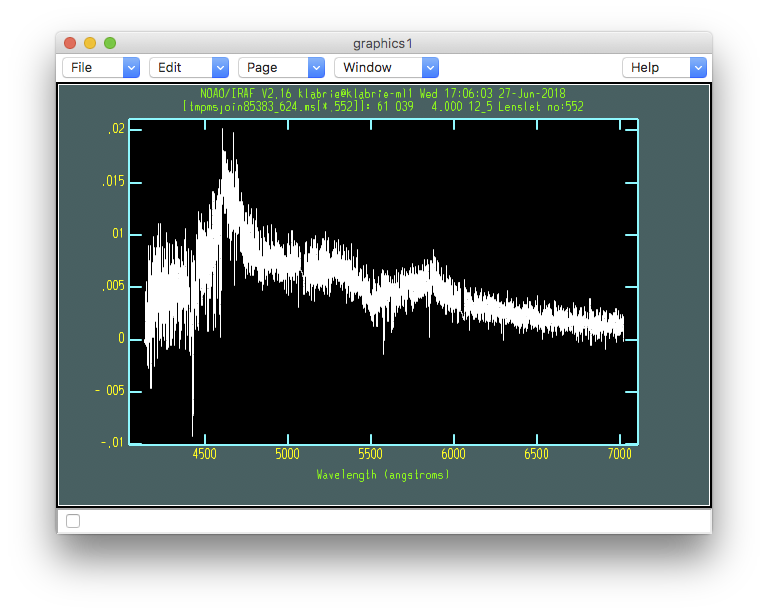
As you can see, the spectrum of the top left source has changed shape. It looks a bit more like a real physical source. It is still not quite right but that is because there is differential atmospheric refraction. We will correct for that in the next chapter when we repackage the data into a data cube.
